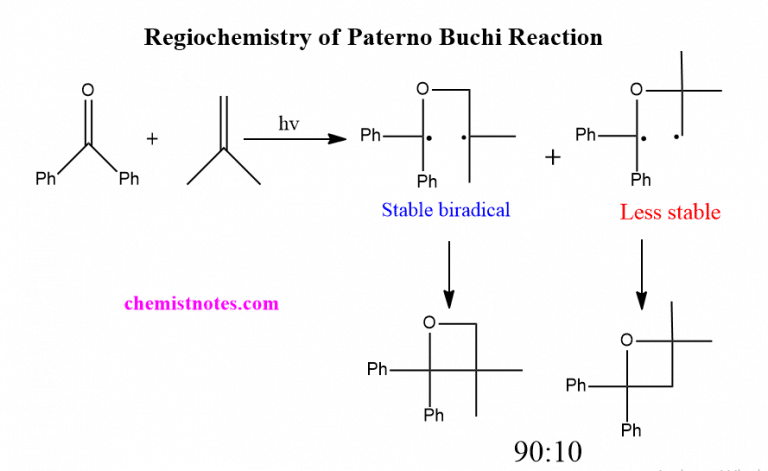
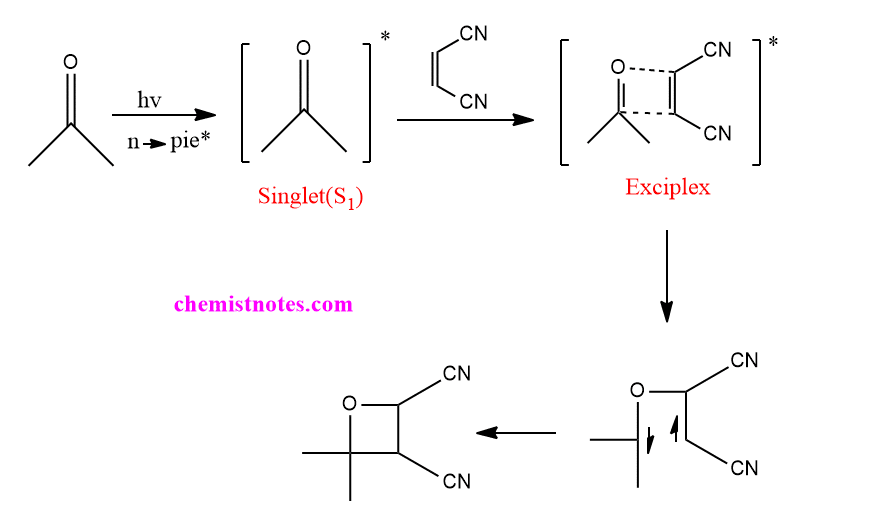
The Paternò–Büchi reaction, named after Emanuele Paternò and George Büchi, who established its basic utility and form, is a photochemical reaction, specifically a 2 2 photocycloaddition, which forms four-membered oxetane rings from an excited carbonyl and reacting with an alkene.
With substrates benzaldehyde and 2-methyl-2-butene the reaction product is a mixture of structural isomers:
Another substrate set is benzaldehyde and furan or heteroaromatic ketones and fluorinated alkenes.
The alternative strategy for the above reaction is called the Transposed Paternò−Büchi reaction.
See also
- Aza Paternò−Büchi reaction - the aza-equivalent of the Paternò–Büchi reaction
- Enone–alkene cycloadditions - photochemical reaction of an enone with an alkene to give a cyclobutene ring unit
References